John Grigg
Senior Lecturer
Department of Ophthalmology, University of Sydney
[email protected]
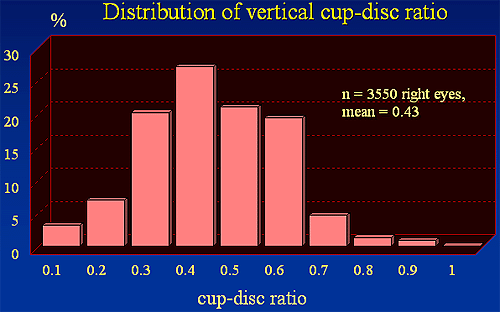
- Vertical cup-to-disc ratio
- Colour and width of neuroretinal rim
- Symmetry between eyes
- Size of the optic disc
|
|
|
- Jonas - characteristic configuration of horizontally oval cup in vertically oval disc is normal.
- Rim with width greatest inferior > superior > nasal > temporal (ISNT rule)
- If not ? Glaucoma - Vertically oval cup
- Concentric enlargement of cup - if increase over time diagnostic
- Asymmetry of cups in both eyes > 0.2
- Focal loss of neuroretinal rim /notch / acquired pit
- Changes in vessels on optic disc: nasalisation, bayoneting, flyover vessels, focal narrowing of vessels, disc haemorrhage
|
|
|
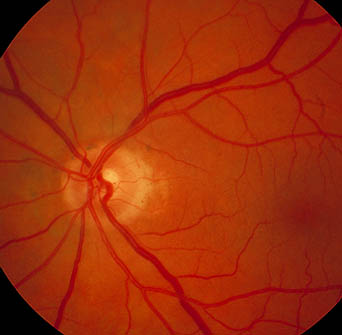
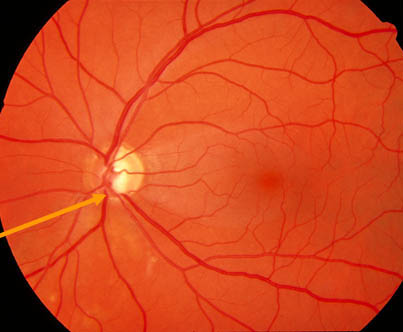
- Nasalisation of vessels
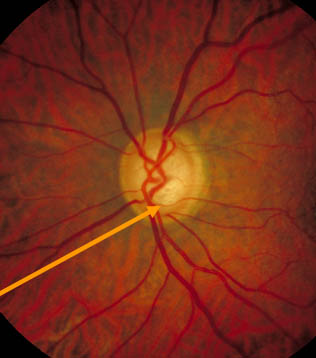
- Bayonetting of vessels
- Baring of circumlinear vessel
- Nasalisation of vessels
- Bayonetting of vessels
- Baring of circumlinear vessel
- Peripapillary atrophy:
- Beta atrophy : increased in glaucoma, particularly where most neuroretinal rim loss - Nerve fibre layer changes:
- grooves, wedge defects, diffuse loss
- Peripapillary atrophy:
- Beta atrophy : increased in glaucoma, particularly where most neuroretinal rim loss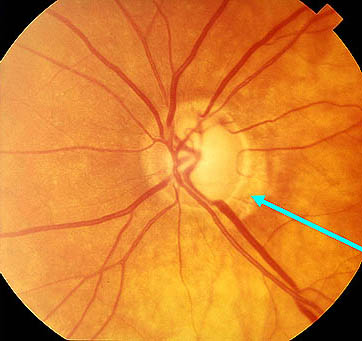
- Nerve fibre layer changes:
- grooves, wedge defects, diffuse loss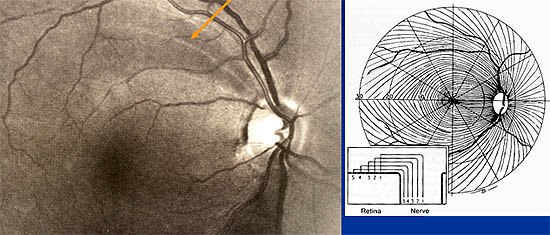
- Disc changes may not be objective unless automated
- (new technology, eg. Heidelberg Retinal Tomograph, Nerve Fibre Layer Analyser) - Visual field progression:
- probability plots, mean deviation, pattern deviation, statpac (Beware short-term fluctuation)
- Progressor - Objective perimetry:
- Accumap
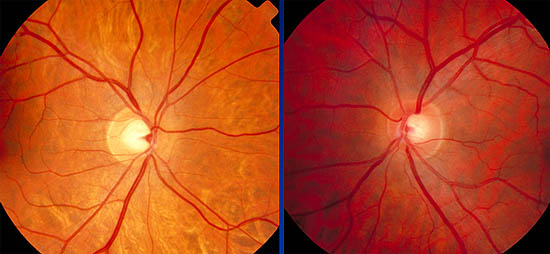
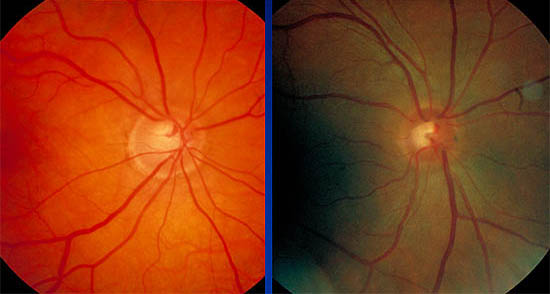
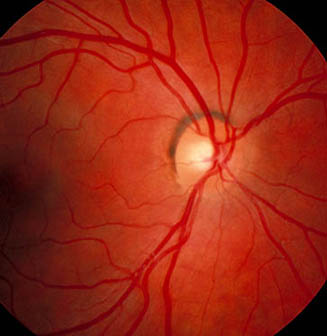
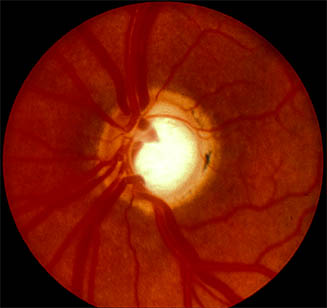
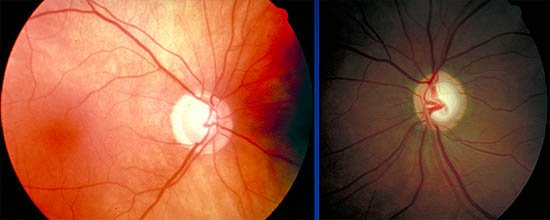
- Cup/disc ratio 0.9
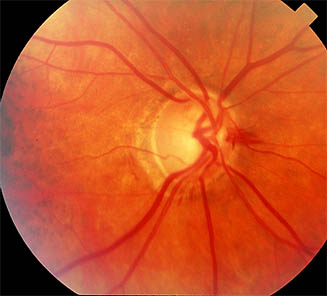
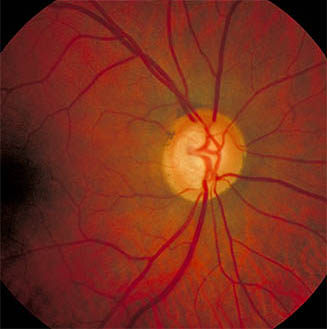
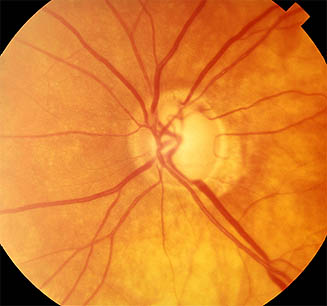
- Superior disc margin Haemorrhage
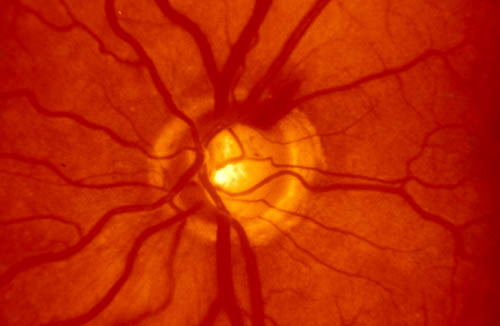
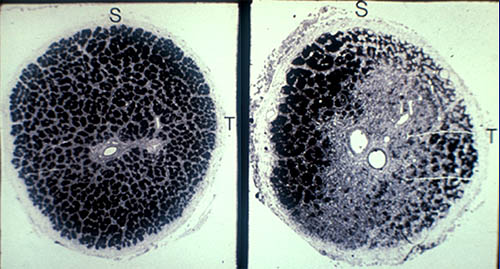

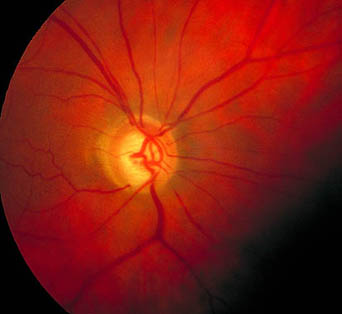
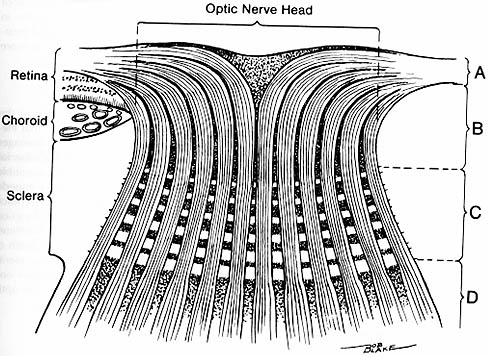
Note the nerve fibre layer arrangement and horizontal demarcation